Assessment of Groundwater Contamination around Bakung Landfill, Lampung, Indonesia Using Geoelectrical Resistivity and Hydrogeochemical Data
Downloads
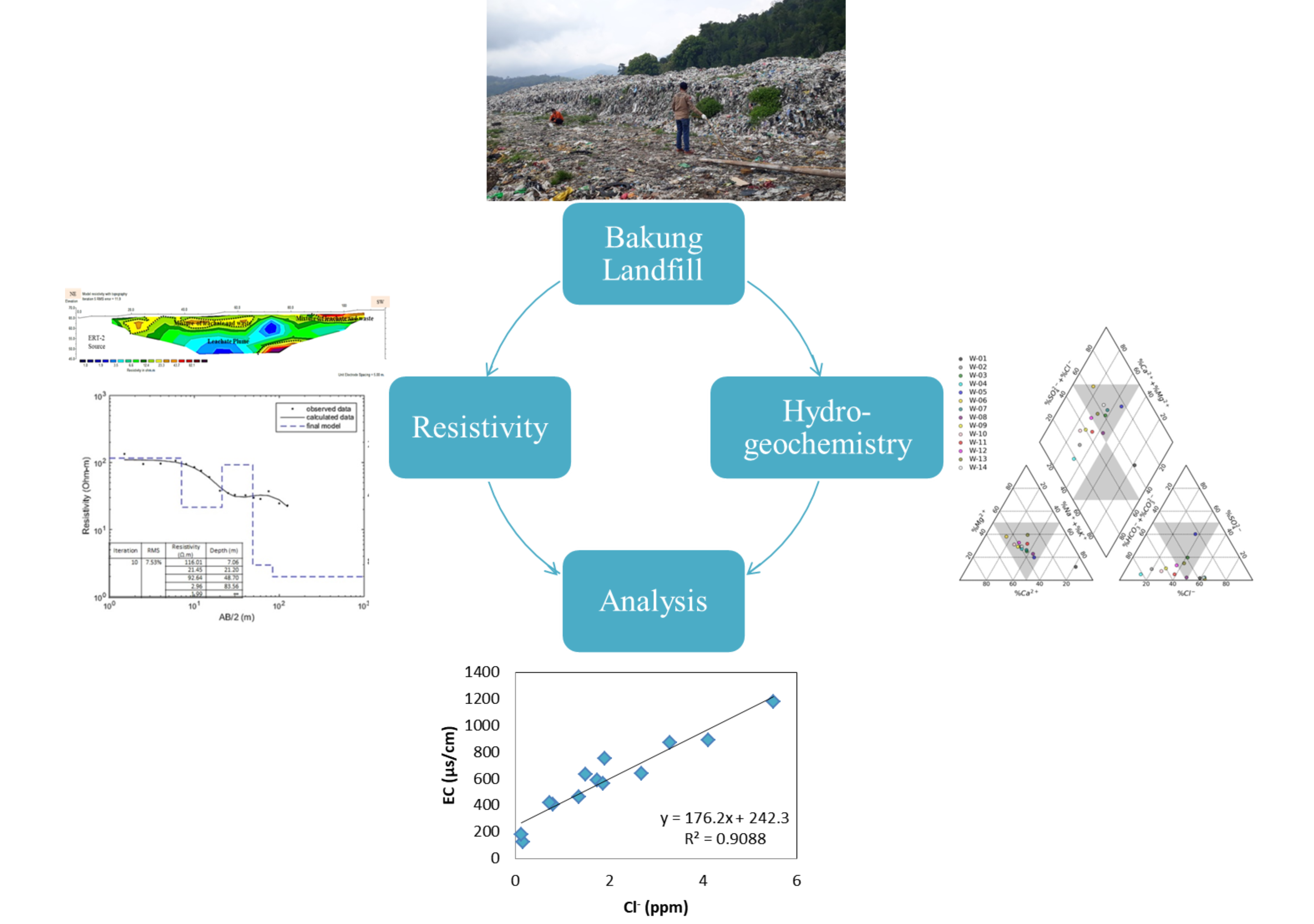
This study investigates groundwater contamination caused by leachate migration at the Bakung landfill during the wet and dry seasons using geoelectrical resistivity and hydrogeochemical methods. The objective is to describe groundwater contamination resulting from leachate and assess groundwater quality from nearby wells along the edge of the Bakung landfill. 1D resistivity sounding (vertical electrical sounding (VES)) survey was conducted at eight sounding points using the Schlumberger configuration, and four lines of 2D resistivity imaging (electrical resistivity tomography (ERT)) were acquired inside and outside the landfill site using the Wenner configuration. The 1D resistivity inversion model show that subsurface resistivity values lower than 40 Ωm are likely associated with tuff rocks, whereas resistivity values greater than 40 Ωm are associated with volcanic breccia. The 2D resistivity imaging model indicates a leachate plume. Migrating into the lower layers of the landfill occurs from the northeast and northwest, suggesting potential contamination of shallow groundwater systems as the landfill ages. The hydrogeochemical assessment of groundwater samples followed APHA standards, identifying hydrogeochemical facies using the Piper diagram and interpreting hydrogeochemical processes using the Gibbs and Gaillardet diagrams. The Piper diagram shows the presence of mixed Ca-Mg-Cl, Ca-HCO3, and Na-Cl facies, with the Na-Cl type found only in well W1, which contains leachate. Contaminated areas exhibit slight increases in ionic concentrations. To prevent contamination from migrating into the aquifer, contaminated zones must be identified.
Aromolaran, O., Fagade, O. E., Aromolaran, O. K., Faleye, E. T., & Faerber, H. (2019). Assessment of groundwater pollution near Aba-Eku municipal solid waste dumpsite. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(12). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7886-1
Butt, N. A., Khan, M. Y., Khattak, S. A., Akhter, G., Ge, Y., Shah, M. T., & Farid, A. (2022). Geophysical and geochemical characterization of solidwaste dumpsite: a case study of Chowa Gujar, Peshawar (Part of Indus Basin). Sustainability, 14(1443). https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031443
Castañeda, S. S., Sucgang, R. J., Almoneda, R. V., Mendoza, N. D. S., & David, C. P. C. (2012). Environmental isotopes and major ions for tracing leachate contamination from a municipal landfill in Metro Manila, Philippines. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 110, 30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2012.01.022
Ekinci, Y. L., & Demirci, A. (2008). A Damped Least-Squares Inversion Program for the Interpretation of Schlumberger Sounding Curves. Journal of Applied Sciences, 8(22), 4070–4078.
Farishi, B. Al, & Setiawan, M. R. (2019). The Mapping of Contamination Potential Surrounding Bakung Landfill Based on Geological Studies. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 258(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/258/1/012022
Gemilang, W. A., Wisha, U. J., & Mardyanto, M. A. (2022). Hydrogeochemical Analysis of Unconfined Groundwater in the Surrounding Salt Farming Areas of Pademawu, Madura, Indonesia. ASEAN Journal on Science and Technology for Development, 39(2), 39–51. https://doi.org/10.29037/ajstd.793
Giang, N. V., Kochanek, K., Vu, N. T., & Duan, N. B. (2018). Landfill leachate assessment by hydrological and geophysical data: case study NamSon, Hanoi, Vietnam. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 20(3), 1648–1662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-018-0732-7
Grisey, E., & Aleya, L. (2016). Assessing the impact of leachate plumes on groundwater quality in the Etueffont landfill (Belfort, France). Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(10). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5725-z
Iryani, D. A., Ikromi, M., Despa, D., & Hasanudin, U. (2019). Characterization of Municipal Solid Waste and Estimation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions at the Bakung Landfill, Bandar Lampung City. Journal of Natural Resources and Environmental Management, 9(2), 218–228. https://doi.org/http://dx.doi.org/10.29244/jpsl.9.2.218-228 (Text in Indonesian)
Kana, A. A., Enebi, A. N., & Kana, A. A. (2022). Hydrogeochemical Processes of Groundwater from Basement Complex Rocks in Keffi, Central Nigeria. Earth Sciences, 11(5), 307–315. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.earth.20221105.17
Khan, A. Y., Ullah, W., Niaz, A., Bibi, T., Imtiaz, M. M., Fiaz, R., … Islam, F. (2024). Integrated geophysical and geospatial techniques for surface and groundwater modeling. Scientific Reports, 14(1), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-76262-8
Kjeldsen, P., Barlaz, M. A., Rooker, A. P., Baun, A., Ledin, A., & Christensen, T. H. (2002). Present and long-term composition of MSW landfill leachate: A review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 32(4), 297–336. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380290813462
Mangga, S. A., Amiruddin, Suwarti, T., Gafoer, S., & Sidarto. (1994). Geology of the Tanjungkarang Quadrangle, Sumatera. Geological Research and Development Center.
Menke, W. (2012). Geophysical data analysis: Discrete inverse theory. In Geophysical Data Analysis: Discrete Inverse Theory (Third). https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(86)90212-x
Niaz, A., Nisar, U. Bin, Khan, S., Faiz, R., Javed, A., Niaz, J., … Bhusal, B. (2023). Flood modelling and its impacts on groundwater vulnerability in sub-Himalayan region of Pakistan: integration between HEC-RAS and geophysical techniques. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2023.2257360
Pamsimas. (2017). Map of the Lampung Groundwater Basin. Retrieved April 1, 2019, from www.new.pamsimas.org website: new.pamsimas.org/Atlas_Cekungan_Air_Tanah/LAMPUNG.jpg (Text in Indonesian)
Pettijohn, F. J. (1975). Sedimentary Rocks, Third Edition (3rd Edition, Vol. 2). New York: Harper and Row.
Reiner, S. R., Laczniak, R. J., Demeo, G. A., Smith, J. L., Elliott, P. E., Nylund, W. E., & Fridrich, C. J. (2002). Ground-water discharge determined from measurements of evapotranspiration, other available hydrologic components, and shallow water-level changes, Oasis Valley, Nye County, Nevada. In US Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report.
Rizka, R., Santoso, D., Warsa, W., Waruwu, P., & Parnadi, W. W. (2023). Application of Vertical Electrical Sounding Method Using Damped Least-Square Inversion for Leachate Identification at Bakung Landfill, Lampung. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 1288(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/1288/1/012033
Surinaidu, L., Nandan, M. J., Kumar, K. M., & Prasad, R. D. (2022). Hydrogeochemical processes and causative pollution sources in the highly urbanized crystalline aquifer system in Southern India. Geosystems and Geoenvironment, 1(3), 100064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geogeo.2022.100064
Tay, C. K. (2021). Hydrogeochemical framework of groundwater within the Asutifi-North District of the Brong-Ahafo Region, Ghana. Applied Water Science, 11(4), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-021-01398-1
Tesoriero, A. J., Spruill, T. B., & Eimers, J. L. (2004). Geochemistry of shallow ground water in coastal plain environments in the southeastern United States: Implications for aquifer susceptibility. Applied Geochemistry, 19(9), 1471–1482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.01.021
Tresoldi, G., Arosio, D., Hojat, A., Longoni, L., Papini, M., & Zanzi, L. (2019). Long-term hydrogeophysical monitoring of the internal conditions of river levees. Engineering Geology, 259(August 2018), 105139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.05.016
Waruwu, P., Rizka, & Warsa. (2022). Pemodelan Distribusi Air Panas Menggunakan Program Inversi Damped Least Square Pada Data Vertical Electrical Sounding Di Desa Way Muli Dan Kunjir. Jurnal Geosaintek, 8(3), 222. https://doi.org/10.12962/j25023659.v8i3.13987.
Copyright (c) 2026 Journal of Engineering and Technological Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.