The Presence of Organochlorine and Organophosphate Pesticide Residue in Groundwater at the Upper Citarum Watershed
Downloads
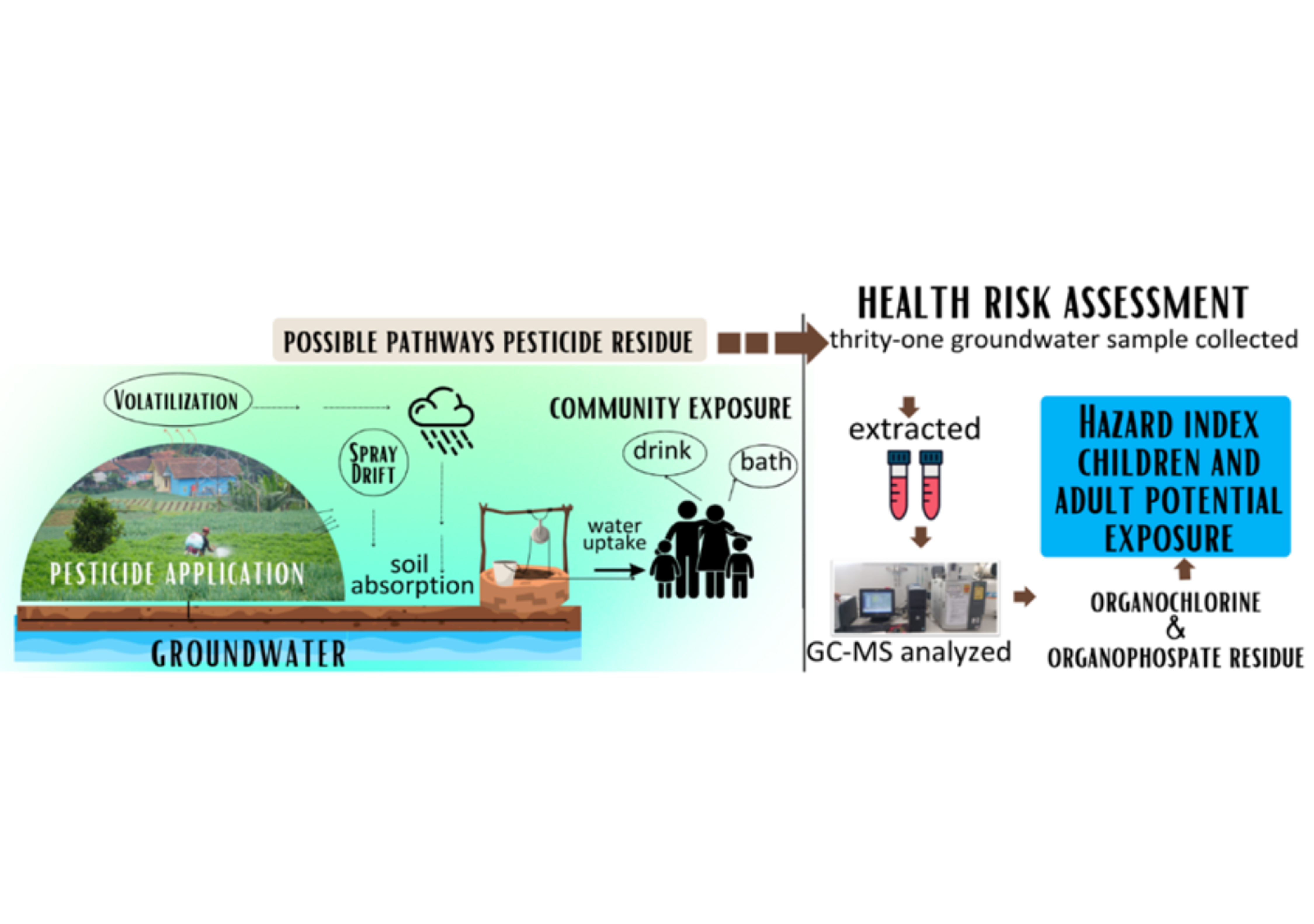
Chemical residue, particularly pesticide from agricultural activities at the Citarum Upper Watershed, is considered an evolving contaminant due to the presence in groundwater samples. Therefore, this qualitative study aims to identify four pesticide residues from organophosphate (OPP) and organochlorine (OCP). Groundwater grab sampling method was applied to collect 31 samples from each location. Extraction was then carried out using the QuEChER preparation technique, followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis. The results showed that Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) had the highest concentration at 0.1062 mg/L. Chlorpyrifos had the highest detection above the limit of detection (LOD) in 13 groundwater samples, with concentrations ranging from 0.0116 to 0.2469 mg/L. Lindane and diazinon were also detected, with maximum concentrations of 0.03209 mg/L and 0.0698 mg/L, respectively. Risk assessment was further carried out to determine the chronic and acute Hazard Quotient (HQ) for all residue. Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and lindane scored > 1 at maximum concentration in adults, while diazinon was at an acceptable level for all scenarios. However, when children-specific parameters were applied, chlorpyrifos demonstrated HQ>1, suggesting additional health risk for children in the area. Immediate studies of pesticide exposure on public health, specifically in children from the site, are essential due to the critical stages in life.
Affum, A. O., Acquaah, S. O., Osae, S. D., & Kwaansa-Ansah, E. E. (2018). Distribution and risk assessment of banned and other current-use pesticides in surface and groundwaters consumed in an agricultural catchment dominated by cocoa crops in the Ankobra Basin, Ghana. Science of the Total Environment, 633, 630–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.129
Ahmad, W., Iqbal, J., Nasir, M. J., Ahmad, B., Khan, M. T., Khan, S. N., & Adnan, S. (2021). Impact of land use/land cover changes on water quality and human health in district Peshawar Pakistan. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 16526. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-96075-3
Al Haj Ishak Al Ali, R., Mondamert, L., Halwani, J., Jandry, J., Nassif, N., Shaban, A., Berjeaud, J. M., & Labanowski, J. (2023). Temporal evolution of organochlorine and organophosphate pesticide residues in wells in the Akkar Region (Lebanon). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(1), 121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10671-y
AOAC. (2007). Official Method 2007.01: Pesticide Residues in Foods by Acetonitrile Extraction and Partitioning with Magnesium Sulfate. Journal of AOAC International, 90(2), 17–26. http://lib3.dss.go.th/fulltext/E_content/1060-3271/2007v90n2.pdf
APVMA. (2024). Malathion. May.
Ardiwinata, A. N., Ginoga, L. N., Sulaeman, E., & Harsanti, E. S. (2020). Pesticide Residue Monitoring on Agriculture in Indonesia. Jurnal Sumberdaya Lahan, 12(2), 133. https://doi.org/10.21082/jsdl.v12n2.2018.133-144 (Text in Indonesian)
Ardiwinata, A. N., & Nursyamsi, D. (2012). Pesticide residues in rice production renters in Central Java. Jurnal Pangan, 21(1), 39–58. https://doi.org/10.33964/jp.v21i1.103
Arias-Estévez, M., López-Periago, E., Martínez-Carballo, E., Simal-Gándara, J., Mejuto, J. C., & García-Río, L. (2008). The mobility and degradation of pesticides in soils and the pollution of groundwater resources. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 123(4), 247–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2007.07.011
ATSDR. (2008). Public Health Statement: Diazinon. Division of Toxicology and Environmental Medicine, September, 460. https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/ToxProfiles/tp86-c1-b.pdf%0Ahttp://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp.asp?id=512&tid=90
ATSDR. (2010). Toxicological Profile for Diazinon (Vol. 10, Nomor Ntp 2005). https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp86-c8.pdf.
Balali-Mood, M. (2009). Neurotoxic Disorders of Organophosphorus Compounds and Their Managements. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 2(1), 205–211.
Bandow, N., Conrad, A., Kolossa-gehring, M., Murawski, A., & Sawal, G. (2020). International Journal of Hygiene and Polychlorinated biphenyls ( PCB ) and organochlorine pesticides ( OCP ) in blood plasma – Results of the German environmental survey for children and adolescents 2014 – 2017 ( GerES V ). International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 224(August 2019), 113426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2019.113426
Bandung Regency Government. (2019). District Profile: Januari 2019. Bandung Regency.
Baqar, M., Sadef, Y., Ahmad, S. R., Mahmood, A., Li, J., & Zhang, G. (2018). Organochlorine pesticides across the tributaries of River Ravi, Pakistan: Human health risk assessment through dermal exposure, ecological risks, source fingerprints and spatio-temporal distribution. Science of the Total Environment, 618, 291–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.234
Beal, S. L. (2001). Ways to fit a PK model with some data below the quantification limit. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics, 28(5), 481–504. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012299115260
Ben Mukiibi, S., Nyanzi, S. A., Kwetegyeka, J., Olisah, C., Taiwo, A. M., Mubiru, E., Tebandeke, E., Matovu, H., Odongo, S., Abayi, J. J. M., Ngeno, E. C., Sillanpää, M., & Ssebugere, P. (2021). Organochlorine pesticide residues in Uganda’s honey as a bioindicator of environmental contamination and reproductive health implications to consumers. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 214, 112094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112094
Benka-Coker, W., Loftus, C., Karr, C., & Magzamen, S. (2020). Association of Organophosphate Pesticide Exposure and a Marker of Asthma Morbidity in an Agricultural Community. Journal of Agromedicine, 25(1), 106–114. https://doi.org/10.1080/1059924X.2019.1619644
Berkowitz, G. S., Wetmur, J. G., Birman-Deych, E., Obel, J., Lapinski, R. H., Goldbold, J. H., Holzman, I. R., & Wolff, M. S. (2004). In Utero pesticides esposure, maternal paraoxonase activity, and head circumference. Environmental Health Perspectives, 112(3), 388–391. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.6414
Bhandari, G., Atreya, K., Scheepers, P. T. J., & Geissen, V. (2020). Concentration and distribution of pesticide residues in soil: Non-dietary human health risk assessment. Chemosphere, 253, 126594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126594
BPS-Statistic of Bandung Regency(2020). Kertasari Regency in Figures. BPS-Statistic of Bandung Regency.(Text in Indonesian).
BPS-Statistic of Bandung Regency (2023). Pacet Subdistrict in Figures. BPS-Statistics of Bandung Regency. (Text in Indonesian).
Burke, R. D., Todd, S. W., Lumsden, E., Mullins, R. J., Mamczarz, J., Fawcett, W. P., Gullapalli, R. P., Randall, W. R., Pereira, E. F. R., & Albuquerque, E. X. (2017). Developmental neurotoxicity of the organophosphorus insecticide chlorpyrifos: from clinical findings to preclinical models and potential mechanisms. Journal of Neurochemistry, 142, 162–177. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14077
Butler-Dawson, J., Galvin, K., Thorne, P. S., & Rohlman, D. S. (2018). Organophosphorus pesticide residue levels in homes located near orchards. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene 15(12), 847–856. https://doi.org/10.1080/15459624.2018.1515489
Canada, H. (2019). Guidance on Natural Organic Matter in Drinking Water. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/consumer-product-safety/pesticides-pest-management/public/consultations/proposed-re-evaluation-decisions/2019/chlorpyrifos/document.html
Carvalho, F. P. (2017). Pesticides, environment, and food safety. Food and Energy Security, 6(2), 48–60. https://doi.org/10.1002/fes3.108
Cohen, S. Z., Creeger, S. M., Carsel, R. F., & Enfield, C. G. (1984). Potential Pesticide Contamination of Groundwater From Agricultural Uses. ACS Symposium Series, 297–325. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-1984-0259.ch018
Commonwealth of Australia. (2002). Environmental Health Risk Assessment. Guidelines for assessing human health risks from environmental hazards. Commonwealth of Australia
Crumpton, T. L., Seidler, F. J., & Slotkin, T. A. (2000). Developmental neurotoxicity of chlorpyrifos in vivo and in vitro: Effects on nuclear transcription factors involved in cell replication and differentiation. Brain Research, 857(1–2), 87–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(99)02357-4
Dar, M. A., Kaushik, G., & Villarreal-Chiu, J. F. (2019). Pollution status and bioremediation of chlorpyrifos in environmental matrices by the application of bacterial communities: A review. Journal of Environmental Management, 239(March), 124–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.03.048
Dehghani, M. H., Kamalian, S., Shayeghi, M., Yousefi, M., Heidarinejad, Z., Agarwal, S., & Gupta, V. K. (2019). High-performance removal of diazinon pesticide from water using multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Microchemical Journal, 145(September 2018), 486–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.10.053
Department of Agriculture. (2018). Agricultural Profile. In Bandung Regency Department of Agriculture Report.
Deviyani, Salami, I. R. S., & Oginawati, K. (2024). Pesticide residue exposure effect on health, growth, and development among children from agricultural area. 7th ETMC E3S Web of Conferences, 485. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202448507009
Dinham, B. (2005). Prolonged exposure to some agricultural pesticides may increase the risk of lung cancer in agricultural workers. Evidence-Based Healthcare and Public Health, 9(3), 203–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ehbc.2005.03.029
EPA. (1987). p , p ’ -Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane ( DDT ); CASRN 50-29-. Iris, 1–16.
EPA. (2000). Parathion Hazard Summary. January, 4. https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2016-09/documents/parathion.pdf
EPA. (2021). EPA Takes Action to Address Risk from Chlorpyrifos and Protect Children’s Health. EPA Press Office. https://www.epa.gov/newsreleases/epa-takes-action-address-risk-chlorpyrifos-and-protect-childrens-health
ESDM. (2019). Groundwater Utilization Must Observe Environmental Balance. https://www.esdm.go.id/en/media-center/news-archives/groundwater-utilization-must-observe-environmental-balance
FAOSTAT. (2022). Pesticides use, pesticides trade and pesticides indicators. Faostat Analytical Brief 46. https://doi.org/10.4060/cc0918en
Foster, S., Chilton, J., Nijsten, G. J., & Richts, A. (2013). Groundwater-a global focus on the “local resource.” Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 5(6), 685–695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosust.2013.10.010
Fricker, M., Tolkovsky, A. M., Borutaite, V., Coleman, M., & Brown, G. C. (2018). Neuronal cell death. Physiological Reviews, 98(2), 813–880. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00011.2017
Furlong, M. A., Herring, A., Buckley, J. P., Goldman, B. D., Daniels, J. L., Engel, L. S., Wolff, M. S., Chen, J., Wetmur, J., Barr, D. B., & Engel, S. M. (2017). Prenatal exposure to organophosphorus pesticides and childhood neurodevelopmental phenotypes. Environmental Research, 158(July), 737–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.07.023
Giácoman Vallejos, G., Castro, I. L., Caballero, C. P., & Sanchéz, A. G. (n.d.). Presence of DDT and Lindane in a Karstic Groundwater Aquifer in Yucatan, Mexico. Groundwater Monitoring and Remediation, 38(2), 68–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwmr.12267
Giddings, J. M., Williams, M. W., Solomon, K. R., & Giesy, J. P. (2014). Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology: risks to aquatic organisms from use of chlorpyrifos in the United States. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 231, 119–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-03865-0_1.
Gilliom, R. J., Barbash, J. E., Crawford, C. G., Hamilton, P. A., Martin, J. D., Nakagaki, N., Nowell, L. H., Scott, J. C., Stackelberg, P. E., Thelin, G. P., & Wolock, D. M. (2006). Pesticides in the Nation’s Streams and Ground Water, 1992 – 2001. In The Quality of Our Nation’s Waters (Revised Fe). U.S. Geological Survey Circular 1291. https://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/cir1291.
Giordano, M. (2009). Global groundwater? Issues and solutions. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 34, 153–178. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.environ.030308.100251
Gonçalves, A. C., Conradi Junior, E., Schwantes, D., Pinheiro, A., Kaufmann, V., & Snak, A. (2023). Environmental fate of chlorpyrifos in Rhodic Ferralsol grown with corn during summer and winter seasons under high-intensity rainfall. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 23(May), 100985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2023.100985
Goumenou, M., & Tsatsakis, A. (2019). Proposing new approaches for the risk characterisation of single chemicals and chemical mixtures: The source related Hazard Quotient (HQS) and Hazard Index (HIS) and the adversity specific Hazard Index (HIA). Toxicology Reports, 6(June), 632–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.06.010
Hossain, M. S., Chowdhury, M. A. Z., Pramanik, M. K., Rahman, M. A., Fakhruddin, A. N. M., & Alam, M. K. (2015). Determination of selected pesticides in water samples adjacent to agricultural fields and removal of organophosphorus insecticide chlorpyrifos using soil bacterial isolates. Applied Water Science, 5(2), 171–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-014-0178-6
Hrynko, I., Kaczyński, P., & Łozowicka, B. (2021). A global study of pesticides in bees: QuEChERS as a sample preparation methodology for their analysis – Critical review and perspective. Science of the Total Environment, 792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148385
Huang, X., Cui, H., & Duan, W. (2020). Ecotoxicity of chlorpyrifos to aquatic organisms: A review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 200(February). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110731
Jaiswal, S., Bara, J. K., Soni, R., & Shrivastava, K. (2017). Bioremediation of Chlorpyrifos Contaminated Soil by Microorganism. International Journal of Environment, Agriculture and Biotechnology, 2(4), 1624–1630. https://doi.org/10.22161/ijeab/2.4.21
Jayaraj, R., Megha, P., & Sreedev, P. (2016). Review Article. Organochlorine pesticides, their toxic effects on living organisms and their fate in the environment. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 9(3–4), 90–100. https://doi.org/10.1515/intox-2016-0012
Jemal, T., Astatke, H., Terfe, A., & Mekonen, S. (2023). Effect of conventional and household water treatment technologies on the removal of pesticide residues in drinking water, Jimma town, Southwestern, Ethiopia. PLoS ONE, 18(7 July), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0288086
Kafilzadeh, F. (2015). Assessment of Organochlorine Pesticide Residues in Water, Sediments and Fish from Lake Tashk, Iran. Achievements in the Life Sciences, 9(2), 107–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.als.2015.12.003
Karan, S., Badawi, N., Jensen, A. M. D., & Rosenbom, A. E. (2021). Impact of fate properties, groundwater fluctuations and the presence of worm burrows on pesticide leaching assessments through golf areas. Environmental Pollution, 289, 117822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117822
Karr, C. (2012). Children’s environmental health in agricultural settings. Journal of Agromedicine 17(20), 127–139. https://doi.org/10.1080/1059924X.2012.658009
Kirdajova, D. B., Kriska, J., Tureckova, J., & Anderova, M. (2020). Ischemia-Triggered Glutamate Excitotoxicity From the Perspective of Glial Cells. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 14(March), 1–27. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2020.00051
Lari, S. Z., Khan, N. A., Gandhi, K. N., Meshram, T. S., & Thacker, N. P. (2014). Comparison of pesticide residues in surface water and ground water of agriculture intensive areas. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 12(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/2052-336X-12-11
Lebov, J. F., Engel, L. S., Richardson, D., Hogan, S. L., Sandler, D. P., & Hoppin, J. A. (2015). Pesticide exposure and end-stage renal disease risk among wives of pesticide applicators in the Agricultural Health Study. Environmental Research, 143, 198–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2015.10.002
Li, L., Zhang, Y., Wang, J., Lu, S., Cao, Y., Tang, C., Yan, Z., & Zheng, L. (2020). History traces of HCHs and DDTs by groundwater dating and their behaviours and ecological risk in northeast China. Chemosphere, 257, 127212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127212
Lipscomb, J. C., Haddad, S., Poet, T., & Krishnan, K. (2012). Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) models in toxicity testing and risk assessment. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 745, 76–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3055-1_6
Liu, B., McConnell, L. L., & Torrents, A. (2001). Hydrolysis of chlorpyrifos in natural waters of the Chesapeake Bay. Chemosphere, 44(6), 1315–1323. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00506-3
Lockridge, O., Verdier, L., & Schopfer, L. M. (2019). Half-life of chlorpyrifos oxon and other organophosphorus esters in aqueous solution. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 311(August), 108788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2019.108788
Lya, T.-K., Ho, T.-D., Behra, P., & Nhu-Trang, T.-T. (2020). Determination of 400 pesticide residues in green tea leaves by UPLC-MS/MS and GC-MS/MS combined with QuEChERS extraction and mixed-mode SPE clean-up method | Elsevier Enhanced Reader. Food Chemistry, 326, 126928. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126928
Menz, C. (2016). O Xygen Delivering Processes in Groundwater and Their Relevance for Iron - Related Well Clogging Processes – a. Journal of Hydrology, 324(1–4), 51–64.
Nandi, N. K., Vyas, A., Akhtar, M. J., & Kumar, B. (2022). The growing concern of chlorpyrifos exposures on human and environmental health. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 185(January), 105138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2022.105138
Oginawati, K., & Pratama, M. A. (2016). Identification and level of organochlorine insecticide contamination in groundwater and iridology analysis for people in Upper Citarum cascade. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 694(1), 012078. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/694/1/012078
Oginawati, K., Susetyo, S. H., Rahmawati, S. I., Kurniawan, S. B., & Abdullah, S. R. S. (2021). Distribution of organochlorine pesticide pollution in water, sediment, mollusk, and fish at Saguling Dam, West Java, Indonesia. Toxicological Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43188-021-00094-1
Oginawati, K., Susetyo, S. H., Rahmawati, S. I., Kurniawan, S. B., & Abdullah, S. R. S. (2022). Distribution of organochlorine pesticide pollution in water, sediment, mollusk, and fish at Saguling Dam, West Java, Indonesia. Toxicological Research, 38(2), 149–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43188-021-00094-1
Olisah, C., & Adams, J. B. (2020). Systematic mapping of organophosphate contaminant (OPC) research trends between 1990 and 2018. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42(11), 3481–3505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00594-3
Pagan, J., Pryor, M., Deepa, R., Grace, J. M., Mbuya, O., Taylor, R., Dickson, J. O., Ibeanusi, V., Chauhan, A., Chen, G., Chen, G., & Anandhi, A. (2020). Sustainable Development Tool Using Meta-Analysis and DPSIR Framework — Application to Savannah River Basin, U.S. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 56(6), 1059–1082. https://doi.org/10.1111/1752-1688.12872
Pérez-Indoval, R., Rodrigo-Ilarri, J., Cassiraga, E., & Rodrigo-Clavero, M. E. (2021). Numerical modeling of groundwater pollution by chlorpyrifos, bromacil and terbuthylazine. Application to the buñol-cheste aquifer (spain). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073511
Prananditya, R., & Oginawati, K. (2016). Identification and distribution of organochlorine pollutant in the ambient air of agricultural area of Citarum Upstream. Jurnal Teknik Lingkungan ITB, 22 (1)(April), 73–82. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.5614/j.tl.2016.22.1.8 (Text in Indonesian)
Qiao, D. (2005). Development of Health Criteria for School Site Risk Assessment Pursuant to Health and Safety Code (Vol. 901, Nomor December).
Qiao, D., Seidler, F. J., & Slotkin, T. A. (2001). Developmental neurotoxicity of chlorpyrifos modeled in vitro: Comparative effects of metabolites and other cholinesterase inhibitors on DNA synthesis in PC12 and C6 cells. Environmental Health Perspectives, 109(9), 909–913. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.01109909
Ragnarsdottir, K. V. (2000). Environmental fate and toxicology of organophosphate pesticides. Journal of the Geological Society, 157(4), 859–876. https://doi.org/10.1144/jgs.157.4.859
Rauh, V. A., Perera, F. P., Horton, M. K., Whyatt, R. M., Bansal, R., Hao, X., Liu, J., Barr, D. B., Slotkin, T. A., & Peterson, B. S. (2012). Brain anomalies in children exposed prenatally to a common organophosphate pesticide. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(20), 7871–7876. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1203396109
Redwar, V. A. (2012 Identification and Distribution of Organochlorine Pesticide Use in Pesticide Mixtures in the Upper Citarum Watershed [Thesis]. Institut Teknologi Bandung, Indonesia.
Rochaddi, B., Sabdono, A., & Zainuri, M. (2019). Preliminary study on the contamination of organophosphate pesticide (chlorpyrifos) in shallow coastal groundwater aquifer of Surabaya and Sidoarjo, East Java Indonesia. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 246(1), 0–5. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/246/1/012079
Rodríguez, D., Barg, G., Queirolo, E. I., Olson, J. R., Mañay, N., & Kordas, K. (2023). Pyrethroid and Chlorpyrifos Pesticide Exposure, General Intellectual Abilities, and Executive Functions of School Children from Montevideo, Uruguay. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20075288
Rother, B. A. P. and H.-A. (2021). Whose Jurisdiction Is Home Contamination_ Para-Occupational ‘Take-Home’ Herbicide Residue Exposure Risks among Forestry Workers’ Families in South Africa _ Enhanced Reader.pdf. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18, 10341. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/103390/ijerph181910341
Rush, T., Liu, X. Q., Hjelmhaug, J., & Lobner, D. (2010). Mechanisms of chlorpyrifos and diazinon induced neurotoxicity in cortical culture. Neuroscience, 166(3), 899–906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.01.025
Safari, M., Ahmadfazeli, A., Vatandoost, H., Karimaee, M., Panahi, D., Shokri, M., Moradian, M., & Soleimani, Z. (2020). Investigating on the residue of organophosphate pesticides in the water of the Hablehrood River, Garmsar, Iran. Journal of Arthropod-Borne Diseases, 14(3), 250–260. https://doi.org/10.18502/jad.v14i3.4558
Sari, P. S., Kesuma, S., & Hartono, A. R. (2024). Perbedaan Kimia Urine Pada Ibu Hamil Trimester 3 dengan Menggunakan Metode Carik Celup dan Metode Otomatis. Borneo Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 4(1), 39–51. https://doi.org/10.21093/bjsme.v3i3.6868
Sarkar, S., Gil, J. D. B., Keeley, J., & Mohring, N. (2021). The use of pesticides in developing countries and their impact on health and the right to food (G. DEFOSSEZ (ed.); Nomor PE 653.622). © European Union, 2021. https://doi.org/doi: 10.2861/28995
Schwantes, D., Celso Gonçalves, A., Conradi Junior, É., Campagnolo, M. A., & Zimmermann, J. (2020). Determination of CHLORPYRIFOS by GC/ECD in water and its sorption mechanism study in a RHODIC FERRALSOL. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 18(1), 149–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-020-00448-1
Shenouda, J., Green, P., & Sultator, L. (2009). An Evaluation of the Inhibition of Human Butyrylcholinesterase and Acetylcholinesterase by the Organophosphate Chlorpyrifos Oxon. Toxilco Appl Pharmacol, 23(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2009.08.014.An
Siriwat, S., Nganchamung, T., Ponrachom, C., Siriwong, W., & Robson, M. G. (2021). Health risk assessment of dermal exposure to Chlorpyrifos among children in agricultural areas in Sakon Nakhon Province, Thailand. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 27(9–10), 2277–2287. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2021.1976102
Sishu, F. K., Tilahun, S. A., Schmitter, P., Assefa, G., & Steenhuis, T. S. (2022). Pesticide Contamination of Surface and Groundwater in an Ethiopian Highlands’ Watershed. Water (Switzerland), 14(21), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213446
Snow, D. D., Chakraborty, P., Uralbekov, B., Satybaldiev, B., Sallach, J. B., Thornton Hampton, L. M., Jeffries, M., Kolok, A. S., & Bartelt-Hunt, S. B. (2020). Legacy and current pesticide residues in Syr Darya, Kazakhstan: Contamination status, seasonal variation and preliminary ecological risk assessment. Water Research, 184, 116141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116141
Srivastav, A. L. (2020). Chemical fertilizers and pesticides: role in groundwater contamination. In Agrochemicals Detection, Treatment and Remediation: Pesticides and Chemical Fertilizers. LTD. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-103017-2.00006-4
Suarez-Lopez, J. R., Himes, J. H., Jacobs, D. R., Alexander, B. H., & Gunnar, M. R. (2013). Acetylcholinesterase activity and neurodevelopment in boys and girls. Pediatrics, 132(6), e1649. https://doi.org/10.1542/PEDS.2013-0108
Sumon, K. A., Rashid, H., Peeters, E. T. H. M., Bosma, R. H., & Van den Brink, P. J. (2018). Environmental monitoring and risk assessment of organophosphate pesticides in aquatic ecosystems of north-west Bangladesh. Chemosphere, 206, 92–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.167
Suryajaya, F. A., Susanto, A., & Irawan, D. E. (2022). Analysis of unconfined groundwater quality and vulnerability to pollution in the kertasari area, bandung regency. PERHIMPUNAN AHLI AIRTANAH INDONESIA (PAAI), November, 8–9. (Text in Indonesian)
Susanti, B. T., Rochaddi, B., Suryono, C. A., & Irwani, I. (2020). Organophosphate pesticide and heavy metals contamination at groundwater in the North Coast region of Central Java and East Java. Jurnal Kelautan Tropis, 23(3), 341–348. https://doi.org/10.14710/jkt.v23i3.9398 (Text in Indonesian)
Tahmasebi, A. A., Tabatabaei, Z., Azhdarpoor, A., & Beni, A. S. (2024). Uncorrected Proof Evaluation of phosphate insecticides and common herbicides : monitoring and risk assessment in water treatment plant , distribution networks , and underground water Uncorrected Proof. 00(0), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.2166/wh.2024.076
Timchalk, C., Nolan, R. J., Mendrala, A. L., Dittenber, D. A., Brzak, K. A., & Mattsson, J. L. (2002). A physiologically based pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic (PBPK/PD) model for the organophosphate insecticide chlorpyrifos in rats and humans. Toxicological Sciences, 66(1), 34–53. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/66.1.34
Tsakiris, I. N., Goumenou, M., Tzatzarakis, M. N., Alegakis, A. K., Tsitsimpikou, C., Ozcagli, E., Vynias, D., & Tsatsakis, A. M. (2015). Risk assessment for children exposed to DDT residues in various milk types from the Greek market. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 75, 156–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2014.11.012
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. (2008). Child-Specific Exposure Factors Handbook. Epa/600/R-06/096F, September, 448.
USEPA. (1983). Risk and hazard assessment. Environmental impact assessment, July, 1–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-6795-3_20
USEPA. (2000a). Chemical Assesment Summary gamma-Hexachlorocyclohexane (gamma-HCH). Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), 2, 1–3.
USEPA. (2000b). Chemical Assesment Summary gamma-Hexachlorocyclohexane (gamma-HCH). Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), 2, 1–3. https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2016-09/documents/lindane.pdf
USEPA. (2000c). Human Health Risk Assesment Chlorpyrifos. Springer Tracts in Civil Engineering, 131.
USEPA. (2003). Appendix A : Background Information for Chlorpyrifos.
USEPA. (2004). Risk assessment guidance for superfund (RAGS). Volume I. Human health evaluation manual (HHEM). Part E. Supplemental guidance for dermal risk assessment. Us Epa, 1(540/R/99/005). https://doi.org/EPA/540/1-89/002
USEPA. (2008). Child-Specific Exposure Factors Handbook. Epa/600/R-06/096F, September, 448.
USEPA. (2008b). Problem Formulation for the Environmental Fate and Ecological Risk, Endangered Species and Drinking Water Assessments in Support of the Registration Review of Diazinon. EPA-HQ-OPP-2008-0351-0003, 41 pages.
USEPA. (2019a). Chlorpyrifos: Revised Human Health Risk Assessment for Registration Review. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 53(9), 1689–1699.
USEPA. (2019b). Guideline for Human Exposure Assessment. Risk Assessment Forum, October, 1–199.
Utami, R. R., Geerling, G. W., Salami, I. R. S., & Notodarmojo, S. (2020). Agricultural Pesticide Use in the Upper Citarum River Basin: Basic Data for Model-Based Risk Management. Journal of Environmental Science and Sustainable Development, 3(2), 12–31. https://doi.org/10.7454/jessd.v3i2.1076
Velis, M., Conti, K. I., & Biermann, F. (2017). Groundwater and human development: synergies and trade-offs within the context of the sustainable development goals. Sustainability Science, 12(6), 1007–1017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-017-0490-9
Wang, D., Singhasemanon, N., & Goh, K. S. (2016). A statistical assessment of pesticide pollution in surface waters using environmental monitoring data: Chlorpyrifos in Central Valley, California. Science of the Total Environment, 571, 332–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.07.159
Wang, D., Singhasemanon, N., & Goh, K. S. (2017). A review of diazinon use, contamination in surface waters, and regulatory actions in California across water years 1992–2014. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(7), 310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6026-z
Wang, H., Cheng, Z., Yuan, H., Zhu, N., Lou, Z., & Otieno, P. (2020). Occurrence of banned and commonly used pesticide residues in concentrated leachate: Implications for ecological risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 710, 136287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136287
Wang, L., Liu, Z., Zhang, J., Wu, Y., & Sun, H. (2016). Chlorpyrifos exposure in farmers and urban adults: Metabolic characteristic, exposure estimation, and potential effect of oxidative damage. Environmental Research, 149, 164–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2016.05.011
Wheater, H. S. (2000). The United Nations World Water Development Report 3: Water in a Changing World. Paris: UNESCO, and London: Earthscan. https://doi.org/10.1142/9781848160682_0002
WHO. (2004). Chlorpyrifos in Drinking-water: Background document for development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality. WHO Report Publication, WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/87.
WHO. (2007). The use of DDT in malaria vector control WHO position statement. WHO Report Publication.http://www.who.int/ipcs/capacity_building/who_statement.pdf
Wołejko, E., Łozowicka, B., Jabłońska-Trypuć, A., Pietruszyńska, M., & Wydro, U. (2022). Chlorpyrifos Occurrence and Toxicological Risk Assessment: A Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19), 12209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912209
Zainuddin, A. H., Wee, S. Y., & Aris, A. Z. (2020). Occurrence and potential risk of organophosphorus pesticides in urbanised Linggi River, Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42(11), 3703–3715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00604-4
Zan, J., Dong, Y., Zhang, W., Xu, W., Li, J., Gao, B., Hu, F., & Wang, Q. (2019). Distribution characteristics of dissolved oxygen and stable isotope compositions of shallow groundwater in the vicinity of an inland nuclear power plant, HK, China. E3S Web of Conferences, 98, 0–4. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/20199809035
Zardosht, Z., Khosravani, F., Rezaei, S., Ghaderi, S., & Hassani, G. (2023). The impact of two insecticides on the pollutant cycle and quality of surface and groundwater resources in the irrigated lands of Yasuj, Iran. Heliyon, 9(6), e17636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17636
Zhang, X., Shen, Y., Yu, X. Y., & Liu, X. J. (2012). Dissipation of chlorpyrifos and residue analysis in rice, soil and water under paddy field conditions. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 78, 276–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.11.036
Zhu, Y., Liu, H., Xi, Z., Cheng, H., & Xu, X. (2005). Organochlorine pesticides (DDTs and HCHs) in soils from the outskirts of Beijing, China. Chemosphere, 60(6 SPEC. ISS.), 770–778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.04.018
Copyright (c) 2026 Journal of Engineering and Technological Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.