Modification of Polylactic Acid with Eggshell Filler as Biodegradable Composite
Downloads
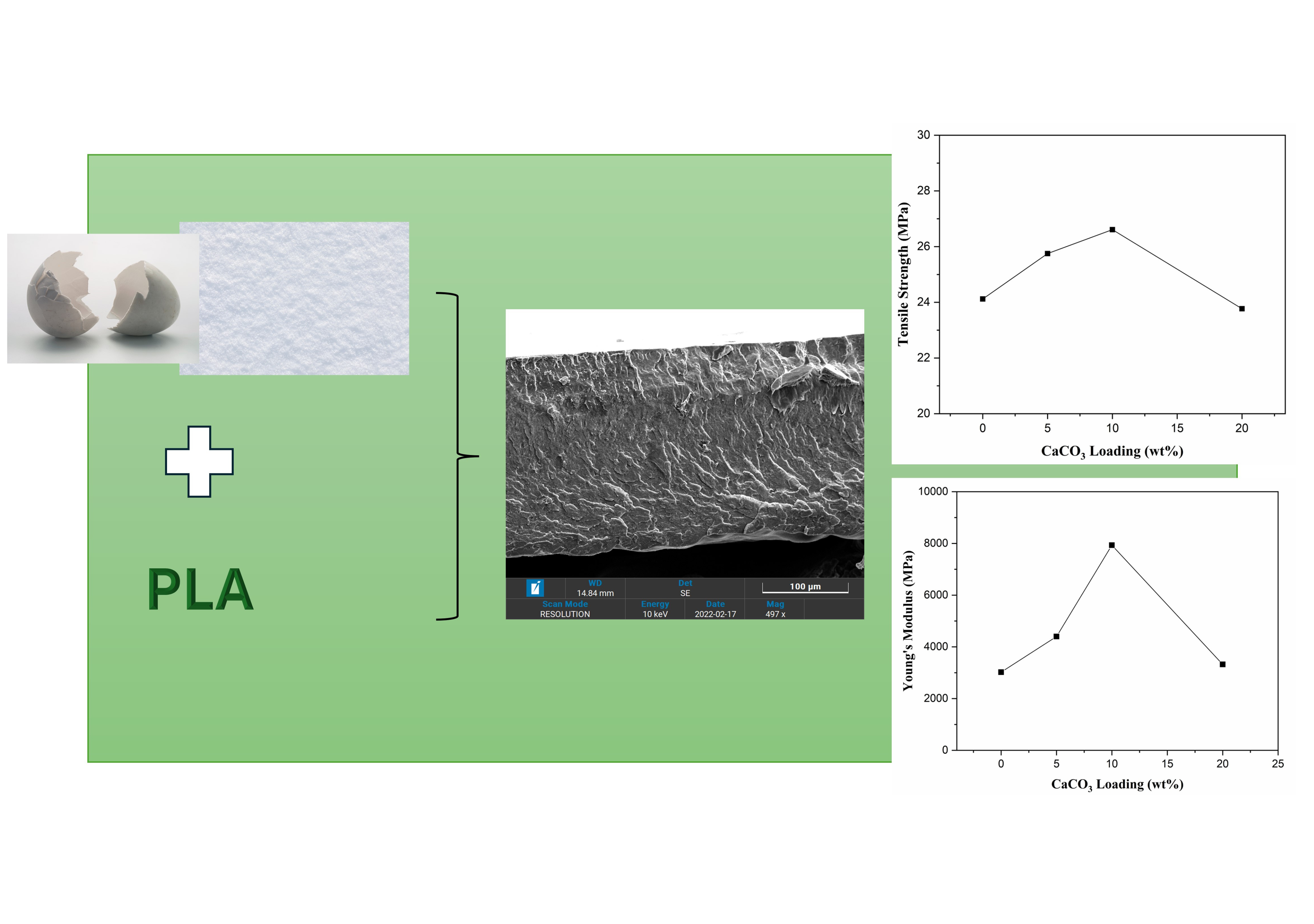
In this study, polylactic acid (PLA) was proposed as a material for producing bioplastics due to the desirable properties, including high processability, low cost, and good transparency. However, the degradation of PLA as a bioplastic remains a significant challenge. To address this problem, PLA was modified by blending with a bio-filler, in the form of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) prepared from eggshell powder (ESP). The CaCO3 filler in form of ESP was incorporated into PLA using the solution casting method. The parameter being varied was the ESP loading, ranging from 0 wt% to 20 wt%. The results showed that the inclusion of eggshell-derived filler in PLA increased tensile strength and Young’s modulus by 10%, from 24.12 to 26.61 MPa, and 162%, from 3022 to 7932 MPa, respectively. The degradability of composite was done through burial test, which the weight of PLA/ESP-20wt% was decreased by 11.11 wt% after 3 weeks. This suggests that eggshell waste has the potential to serve as an effective filler to improve the mechanical strength and degradation of PLA.
Aframehr, W. M., Molki, B., Heidarian, P., Behzad, T., Sadeghi, M., & Bagheri, R. (2017). Effect of calcium carbonate nanoparticles on barrier properties and biodegradability of polylactic acid. Fibers and Polymers, 18(11), 2041-2048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-017-6853-0
Ansink, E., Wijk, L., & Zuidmeer, F. (2022). No clue about bioplastics. Ecological Economics, 191, 107245. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2021.107245
Balla, E., Daniilidis, V., Karlioti, G., Kalamas, T., Stefanidou, M., Bikiaris, N. D., . . . Bikiaris, D. N. (2021). Poly(lactic Acid): A Versatile Biobased Polymer for the Future with Multifunctional Properties—From Monomer Synthesis, Polymerization Techniques and Molecular Weight Increase to PLA Applications. Polymers, 13(11), 1822.
Bezirhan, E., & Bilgen, H. D. (2015). A Review: Investigation of Bioplastics. Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 9, 188-192. https://doi.org/10.17265/1934-7359/2015.02.007
Bijarimi, M., Alya Azlan, S., Norazmi, M., Normaya, E., & Mat Desa, M. S. Z. (2023). Sustainable green poly(lactic acid) (PLA)/eggshell powder (ESP) biocomposites. Materials Today: Proceedings, 85, 83-86. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2023.05.265
Chen, H. L., Nath, T. K., Chong, S., Foo, V., Gibbins, C., & Lechner, A. M. (2021). The plastic waste problem in Malaysia: management, recycling and disposal of local and global plastic waste. SN Applied Sciences, 3(4), 437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-021-04234-y
Cree, D., & Soleimani, M. (2023). Bio-Based White Eggshell as a Value-Added Filler in Poly(Lactic Acid) Composites. Journal of Composites Science, 7(7), 278.
de França, J. O., da Silva Valadares, D., Paiva, M. F., Dias, S. C., & Dias, J. A. (2022). Polymers Based on PLA from Synthesis Using D,L-Lactic Acid (or Racemic Lactide) and Some Biomedical Applications: A Short Review. Polymers, 14(12), 2317.
Ding, J., Li, X., Ren, Y., & Zhao, X. (2023). Preparation of PLA/Lignin-CaCO3 composites by carbon dioxide carbonization and subsequent melt blending method. Materials Letters, 336, 133883. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2023.133883
Dziuba, R., Kucharska, M., Madej-Kiełbik, L., Sulak, K., & Wiśniewska-Wrona, M. (2021). Biopolymers and Biomaterials for Special Applications within the Context of the Circular Economy. Materials (Basel), 14(24), 7704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247704
Folino, A., Karageorgiou, A., Calabrò, P. S., & Komilis, D. (2020). Biodegradation of Wasted Bioplastics in Natural and Industrial Environments: A Review. Sustainability, 12(15), 6030.
Gbadeyan, O. J., Linganiso, L. Z., & Deenadayalu, N. (2022). Thermomechanical characterization of bioplastic films produced using a combination of polylactic acid and bionano calcium carbonate. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 15538. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-20004-1
Geyer, R., Jambeck, J. R., & Law, K. L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Science Advances, 3(7), e1700782. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1700782
Gomez-Gamez, A. B., Yebra-Rodriguez, A., Peñas-Sanjuan, A., Soriano-Cuadrado, B., & Jimenez-
Millan, J. (2020). Influence of clay percentage on the technical properties of montmorillonite/polylactic acid nanocomposites. Applied Clay Science, 198, 105818. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2020.105818
Guo, Z., Song, W., Song, Y., Liu, X., Guo, Z., & Sun, D. (2024). Effects of Nano- and Micro-sized Calcium Carbonate on the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Poly(lactic acid)/Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) with Bi-continuous Phases. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 32(1), 384-398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-023-02953-4
Guo, Z., Song, W., Wei, X., Feng, Y., Song, Y., Guo, Z., . . . Song, S. (2023). Effect of matrix composition on the performance of calcium carbonate filled poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) composites. e-Polymers, 23(1), 20230026. https://doi.org/doi:10.1515/epoly-2023-0026
Han, J.-s., Kwon, S.-j., Kim, S. Y., & Oh, K. (2024). Chitin/calcium carbonate complex microparticles and their effects on polylactic acid composite films. Cellulose, 31(10), 6123-6139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05967-w
Hanumantharaju, H. G., Prashanth, K. P., Ramu, B., Venkatesh, N., & Chethan, G. R. (2023). 3D Printing of Biopolymer Composites Investigation on Effect of Egg Shell Particles on Polylactic Acid Matrix. Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry, 13(3), Article 251. https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC133.251
Homavand, A., Cree, D. E., & Wilson, L. D. (2024). Polylactic Acid Composites Reinforced with Eggshell/CaCO3 Filler Particles: A Review. Waste, 2(2), 169-185.
Jiang, D., Ning, F., & Wang, Y. (2021). Additive manufacturing of biodegradable iron-based particle reinforced polylactic acid composite scaffolds for tissue engineering. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 289, 116952. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.116952
Lanzón, M., Madrid-Mendoza, J. A., Navarro-Moreno, D., & García-Vera, V. E. (2023). Use of eggshell waste: A green and effective method for the synthesis of pure calcium hydroxide suspensions. Construction and Building Materials, 377, 131106. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.131106
Leluk, K., Frąckowiak, S., Ludwiczak, J., Rydzkowski, T., & Thakur, V. K. (2020). The Impact of Filler Geometry on Polylactic Acid-Based Sustainable Polymer Composites. Molecules, 26(1), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26010149
Li, X., Lin, Y., Liu, M., Meng, L., & Li, C. (2023). A review of research and application of polylactic acid composites [https://doi.org/10.1002/app.53477]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 140(7), e53477. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1002/app.53477
Naser, A. Z., Deiab, I., & Darras, B. M. (2021). Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), green alternatives to petroleum-based plastics: a review. RSC Adv, 11(28), 17151-17196. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra02390j
Orisekeh, D. K., Corti, G., & Jahan, M. P. (2025). Enhancing thermo-mechanical properties of additively manufactured PLA using eggshell microparticle fillers. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 133, 782-797. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2024.11.095
Owuamanam, S., & Cree, D. (2020). Progress of Bio-Calcium Carbonate Waste Eggshell and Seashell Fillers in Polymer Composites: A Review. Journal of Composites Science, 4(2), 70.
Perera, Y. S., Naaib, M., Ariyasinghe, N., & Abeykoon, C. (2025). Investigation of the effect of extrusion process parameters and filler loading on the performance of LDPE composites reinforced with eggshell powder. Composites Part C: Open Access, 16, 100561. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcomc.2025.100561
Reddyvari, R., Lu, S., Kosuri, P., & Amalaradjou, M. A. (2025). Incorporation of probiotics in post-harvest wash treatments reduces Salmonella contamination and improves egg safety. Poultry Science, 104(6), 105146. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2025.105146
Ritchie, H. R., Max. (2018). Plastic Pollution. Published online at OurWorldinData.org. Retrieved from: 'https://ourworldindata.org/plastic-pollution
Roy, K., Debnath, S., Raengthon, N., & Potiyaraj, P. (2019). Understanding the reinforcing efficiency of waste eggshell‐derived nano calcium carbonate in natural rubber composites with maleated natural rubber as compatibilizer. Polymer Engineering & Science, 59. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.25127
Shaikh, S., Yaqoob, M., & Aggarwal, P. (2021). An overview of biodegradable packaging in food industry. Curr Res Food Sci, 4, 503-520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crfs.2021.07.005
Shamsuddin, I. (2017). Bioplastics as Better Alternative to Petroplastics and Their Role in National Sustainability: A Review. Advances in Bioscience and Bioengineering, 5, 63. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.abb.20170504.13
Sharma, R., Mehrotra, N., Singh, I., & Pal, K. (2024). Development and characterization of PLA nanocomposites reinforced with bio-ceramic particles for orthognathic implants: Enhanced mechanical and biological properties. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 282, 136751. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.136751
Sharma, R. K., & Kumar, S. R. (2024). Investigation of the mechanical, thermal and wear properties of eggshell/PLA composites. International Polymer Processing, 39(3), 308-316. https://doi.org/doi:10.1515/ipp-2024-0005
Sulimai, N. H., Rusop, M., Alrokayan, S. A. H., & Khan, H. A. (2016). A review: Different methods producing different particles size and distribution in synthesis of calcium carbonate nano particles. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1733(1), 020057. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4948875
Yao, J., Hu, H., Sun, Z., Wang, Y., Huang, H., Gao, L., . . . Xiong, C. (2021). Synchronously Strengthen and Toughen Polypropylene Using Tartaric Acid-Modified Nano-CaCO(3). Nanomaterials (Basel), 11(10), 2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102493
Zarei, M., Hosseini Nikoo, M. M., Alizadeh, R., & Askarinya, A. (2024). Synergistic effect of CaCO3 addition and in-process cold atmospheric plasma treatment on the surface evolution, mechanical properties, and in-vitro degradation behavior of FDM-printed PLA scaffolds. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 149, 106239. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2023.106239
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Engineering and Technological Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.