Data-driven Analysis and Optimization of Combined Cycle Power Plants using Machine Learning Models
Downloads
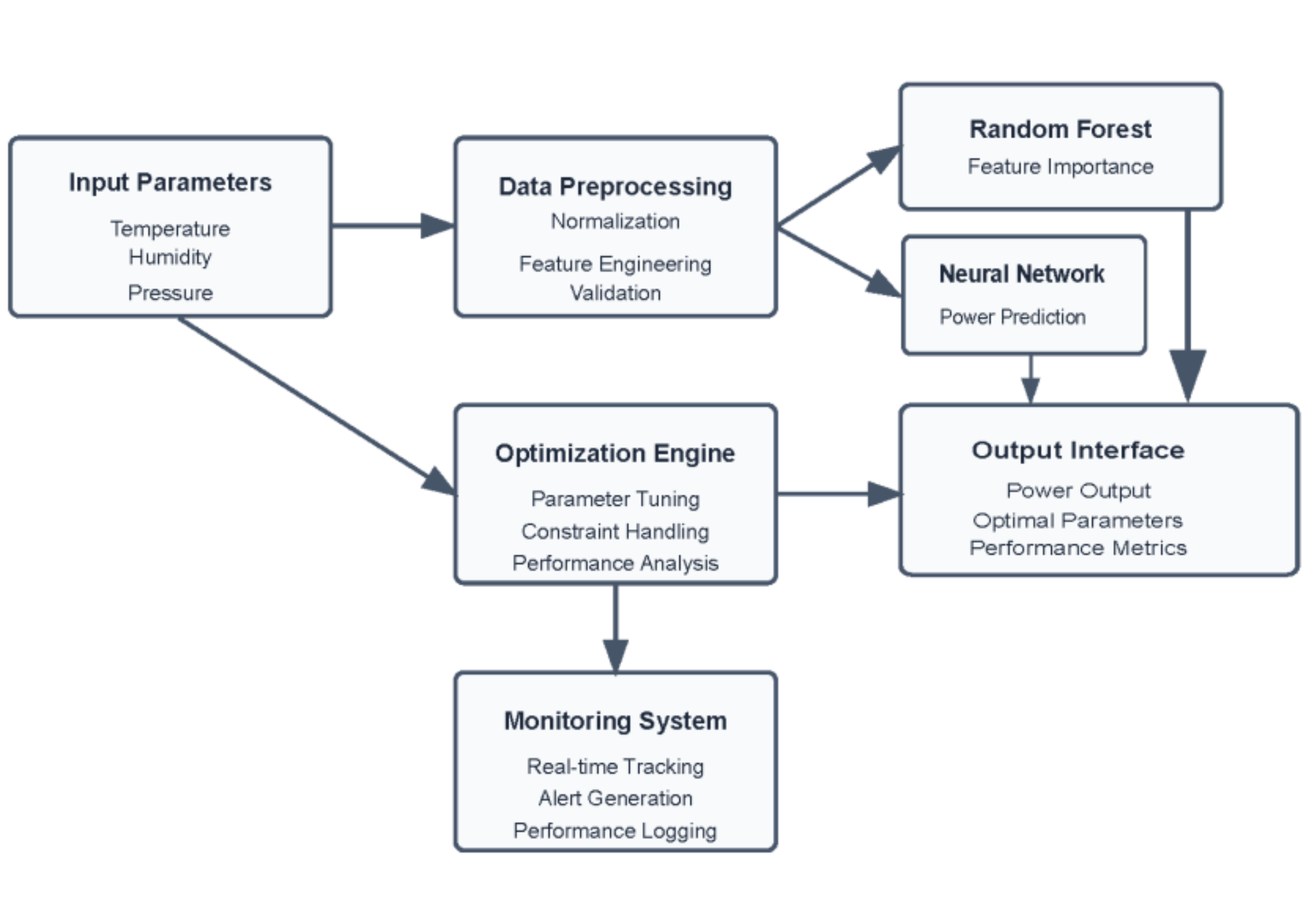
The current global energy demand relies more on Combined Cycle Power Plants (CCPPs) for their high efficiency and reduced environmental footprint. However, the performance of these plants is very sensitive to several environment parameters including temperature, pressure, humidity, and exhaust vacuum. This paper is intended to use machine learning (ML) approach to model and optimize CCPP energy production based on these factors. The proposed method uses a dataset with hourly environmental measurements, to provide detailed analysis using ML techniques including Random Forests and Neural Networks to identify any potential nonlinear relationships and predict energy output. The results showed that ambient temperature has the most significant influence on energy production, followed by vacuum, pressure, and humidity. In addition, this paper also highlighted optimal environmental conditions that maximize energy output, which can help and support power plant operators in optimizing their operation factors. In summary, the recommendations and outcomes of this paper provide necessary steps for integrating advanced ML techniques into CCPP operations, enhancing both efficiency and sustainability.
Akdemir, B. (2016). Prediction of hourly generated electric power using artificial neural network for combined cycle power plant. International Journal of Electrical Energy, 4(2), 91-95.
Ali, H. M. (2021). Prediction of energy generated from composite cycle power plant in smart cities. Periodicals of Engineering and Natural Sciences, 9(4), 207-213.
Andjelić, N., Lorencin, I., Mrzljak, V., & Car, Z. (2024). On the application of symbolic regression in the energy sector: Estimation of combined cycle power plant electrical power output using genetic programming algorithm. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 133, 108213.
Arrieta, F. R. P., & Lora, E. E. S. (2005). Influence of ambient temperature on combined-cycle power-plant performance. Applied Energy, 80(3), 261-272.
Asghar, A., Ratlamwala, T. A. H., Kamal, K., Alkahtani, M., Mohammad, E., & Mathavan, S. (2023). Sustainable operations of a combined cycle power plant using artificial intelligence based power prediction. Heliyon, 9(9), e19562. DOI10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19562.
Bagnasco, A., Delfino, B., Denegri, G. B., & Massucco, S. (1998). Management and dynamic performances of combined cycle power plants during parallel and islanding operation. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 13(2), 194-201.
Bandić, L., Hasičić, M., & Kevrić, J. (2020). Prediction of power output for combined cycle power plant using random decision tree algorithms and ANFIS. In Advanced Technologies, Systems, and Applications IV—Proceedings of the International Symposium on Innovative and Interdisciplinary Applications of Advanced Technologies (IAT 2019) (pp. 406-416).
Chary, D. (2021). Prediction of full load electrical power output of a base load operated combined cycle power plant using machine learning methods. Journal for Innovative Development in Pharmaceutical and Technical Science, 4, 63-66.
Chu, N., & Ma, W. (2024). Exploration of the influencing factors of intelligent robots on college network education in the all-media era. Journal of Engineering and Technological Sciences, 56(3), 414-424.
Danish, M. S. S., Nazari, Z., & Senjyu, T. (2023). AI-coherent data-driven forecasting model for a combined cycle power plant. Energy Conversion and Management, 286, 117063.
Dutta, S., & Ghosh, S. (2021). Predicting electrical power output in a combined cycle power plant—A statistical approach. International Journal of Energy Engineering, 11(2), 17-26.
Fantozzi, F., & Desideri, U. (1998). Simulation of power plant transients with artificial neural networks: Application to an existing combined cycle. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part A: Journal of Power and Energy, 212(5), 299-313.
Kabengele, K. T., Tartibu, L. K., & Olayode, I. O. (2022). Modeling of a combined cycle power plant performance using artificial neural network model. In 2022 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, Computing and Data Communication Systems (icABCD) (pp. 1-7). IEEE.
Kaewprapha, P., Prempaneerach, P., Singh, V., Tinikul, T., & Intarangsi, N. (2022). Machine learning approaches for estimating the efficiency of combined cycle power plant. In 2022 International Electrical Engineering Congress (iEECON) (pp. 1-4). IEEE.
Kaggle. (2024). Power plant data—Predict the net hourly electrical energy output (PE). https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/gauravduttakiit/power-plant-data
Khalid, S., Hwang, H., & Kim, H. S. (2021). Real-world data-driven machine-learning-based optimal sensor selection approach for equipment fault detection in a thermal power plant. Mathematics, 9(21), 2814.
Kotowicz, J., & Brzęczek, M. (2018). Analysis of increasing efficiency of modern combined cycle power plant: A case study. Energy, 153, 90-99.
Manuel, H. N. N., Kehinde, H. M., Agupugo, C. P., & Manuel, A. C. N. (2024). The impact of AI on boosting renewable energy utilization and visual power plant efficiency in contemporary construction. World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews, 23(2), 1333-1348.
Ntantis, E. L., & Xezonakis, V. (2024). Optimization of electric power prediction of a combined cycle power plant using innovative machine learning technique. Optimal Control Applications and Methods, 45(5), 2218-2230.
Saeed, M. A., El-Kenawy, E. M., Ibrahim, A., Abdelhamid, A. A., Eid, M. M., Karim, F. K., ... Abualigah, L. (2023). Electrical power output prediction of combined cycle power plants using a recurrent neural network optimized by waterwheel plant algorithm. Frontiers in Energy Research, 11, 1234624.
Sharma, H., Marinovici, L., Adetola, V., & Schaef, H. T. (2023). Data-driven modeling of power generation for a coal power plant under cycling. Energy and AI, 11, 100214.
Siddiqui, R., Anwar, H., Ullah, F., Ullah, R., Rehman, M. A., Jan, N., & Zaman, F. (2021). Power prediction of combined cycle power plant (CCPP) using machine learning algorithm-based paradigm. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2021(1), 9966395.
Wang, S., Liu, Z., Cordtz, R., Imran, M., & Fu, Z. (2019). Performance prediction of the combined cycle power plant with inlet air heating under part load conditions. Energy Conversion and Management, 200, 112063.
Waqar, M. A., Uddin, G. M., Asghar, S., Ahmad, M., Hassan, M. K., & Jamil, H. (2024). Driving towards net-zero from the energy sector: Leveraging machine intelligence for robust optimization of coal and combined cycle gas power stations. Energy Conversion and Management, 314, 118645.
Xezonakis, V., Samuel, O. D., & Enweremadu, C. C. (2024). Modeling and output power estimation of a combined gas plant and a combined cycle plant using an artificial neural network approach. Journal of Engineering, 2024(1), 5540010.
Yi, Q., Xiong, H., & Wang, D. (2023). Predicting power generation from a combined cycle power plant using transformer encoders with DNN. Electronics, 12(11), 2431. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12112431
Zamani, A. A., Tavakoli, S., Etaati, N., & Jahangoshai Rezaee, M. (2024). Prediction of electricity load generated by combined cycle power plants using integration of machine learning methods and HGS algorithm. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 120, 109641.
Zwebek, A. I. (2002). Combined cycle performance deterioration analysis [Doctoral dissertation, Cranfield University]
Copyright (c) 2026 Journal of Engineering and Technological Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.