Experimental Investigation and Prediction of Combustion Parameters using Machine Learning in Ethanol - Gasoline Blended Engines
Downloads
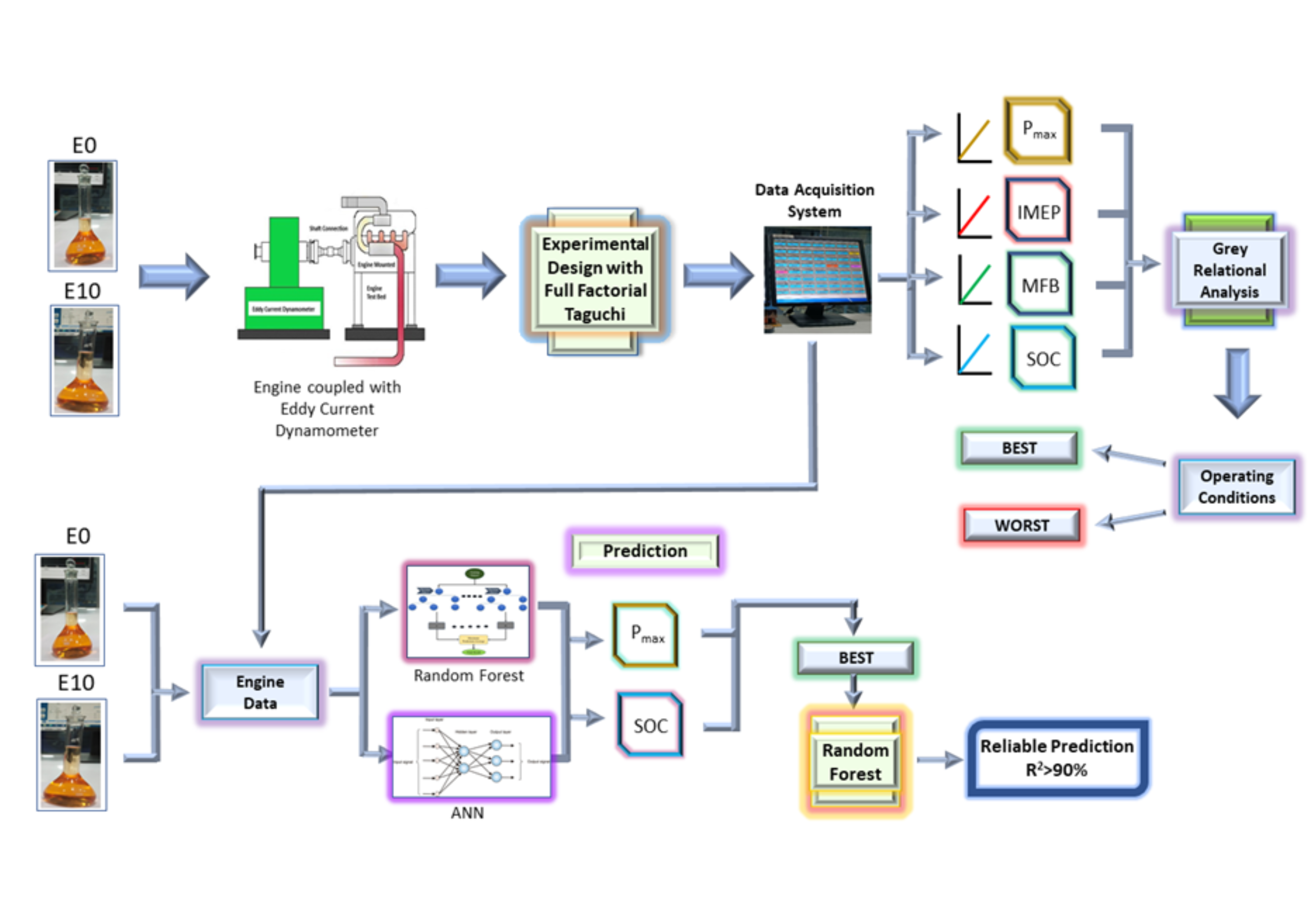
Alternative fuels play an important role in eco-friendly transport solutions. Wider adoption of alternative blended fuels in automobiles is dependent on a better understanding of the blended fuel engine characteristics. This paper presents an experimental investigation on the part load combustion characteristics of a multi cylinder spark ignition (SI) engine fueled by E0 and E10 ethanol blends. Full factorial Taguchi experimental design was employed to include multi-level engine speed (rpm) and load (throttle %) variations. High-speed data acquisition was used to record combustion parameters viz. maximum pressure (Pmax), indicative mean effective pressure (IMEP), start of combustion (SOC), mass burn fraction (MBF) and burn duration (Brn_drn) over 300 combustion cycles for each experimental run. Grey Relational Analysis (GRA) was used to determine the optimum best and worst engine operating conditions based on Pmax, IMEP, MBF and Brn_drn. Cycle-to-cycle variations of Pmax were also examined in detail to identify the worst engine operating condition. Random Forest machine learning algorithm was employed to accurately model Pmax and SOC in terms of the engine part load operating conditions. This model can be used to predict Pmax and SOC characteristics of an E0/E10 fueled SI engine under different operating conditions, eliminating the need for extensive testing
Ahmed, A. M., Youssef, I., & Mourad, M. (2017). The Influence of Ethanol – Gasoline Blends on Performance Characteristics of Engine Generator Set. American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER), 6(9), 71–77.
Al-Aboodi, A. H., Al-Abadi, A. M., & T. Ibrahim, H. (2017). A Committee Machine with Intelligent Systems for Estimating Monthly Mean Reference Evapotranspiration in an Arid Region. Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology. https://doi.org/10.19026/rjaset.14.5131
Bawase, M. A., & Thipse, D. S. S. (2021). Impact of 20% Ethanol-blended Gasoline (E20) on Metals and Non-metals used in Fuel-system Components of Vehicles. ARAI Journal of Mobility Technology. https://doi.org/10.37285/ajmt.1.0.1
Chen, H., Xu, M., Hung, D. L. S., & Zhuang, H. (2014). Cycle-to-cycle variation analysis of early flame propagation in engine cylinder using proper orthogonal decomposition. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2014.06.017
Deng, B., Hou, K., Duan, X., & Xu, Z. (2021). The correlation between intake fluctuation and combustion CCV (cycle-to-cycle variations) on a high speed gasoline engine: A wide range operating condition study. Fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121336
Duan, X., Deng, B., Liu, Y., Li, Y., & Liu, J. (2021). Experimental study the impacts of the key operating and design parameters on the cycle-to-cycle variations of the natural gas SI engine. Fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119976
Elumalai, R., Sumathy, S., K, R., Akhtar, M. N., P V, E., Khan, S. A., Gupta, M. S., & Asif, M. (2024). Experimental investigation and gray relational optimization of engine parameters to improve the output characteristics of an ammonia biodiesel powered dual fuel combustion engine. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2024.104197
Elumalai, P. V., Krishna Moorthy, R., Parthasarathy, M., Samuel, O. D., Owamah, H. I., Saleel, C. A., Enweremadu, C. C., Sreenivasa
Reddy, M., & Afzal, A. (2022). Artificial neural networks model for predicting the behavior of different injection pressure characteristics powered by blend of biofuel-nano emulsion. Energy Science and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1002/ese3.1144
Granet, V., Vermorel, O., Lacour, C., Enaux, B., Dugué, V., & Poinsot, T. (2012). Large-Eddy Simulation and experimental study of cycle-to-cycle variations of stable and unstable operating points in a spark ignition engine. Combustion and Flame. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2011.11.018
Hanuschkin, A., Zündorf, S., Schmidt, M., Welch, C., Schorr, J., Peters, S., Dreizler, A., & Böhm, B. (2021). Investigation of cycle-to-cycle variations in a spark-ignition engine based on a machine learning analysis of the early flame kernel. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proci.2020.05.030
Heywood, J. B. (1988). Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals 2nd Edition. Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals.
Kavathekar, K. P., Thipse, S. S., Rairikar, S. D., Sonawane, S. B., Sutar, P. S., & Bandyopadhyay, D. (2021). Study of Effect on Engine Performance Using 15% HCNG Blend Versus CNG Using a Simulation Approach. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3639-7_25
Kazmouz, S. J., Haworth, D. C., Lillo, P., & Sick, V. (2021). Large-eddy simulations of a stratified-charge direct-injection spark-ignition engine: Comparison with experiment and analysis of cycle-to-cycle variations. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proci.2020.08.035
Kheiralla, A. F., & Tola, E. (n.d.). Performance of ethanol-gasoline blends of up to E35. Advances in Bioresearch. https://doi.org/10.15515/abr.0976-4585.8.5.130140
Khoshkangini, R., Mashhadi, P., Tegnered, D., Lundström, J., & Rögnvaldsson, T. (2023). Predicting Vehicle Behavior Using Multi-task Ensemble Learning. Expert Systems with Applications. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.118716
Kim, J., & Min, K. (2023). Analysis of combustion cyclic variation in a lean burn spark-ignited engine using large eddy simulation. Fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2023.127886
Kodancha, P., Pai, A., Kini, C. R., & Bayar, R. K. (2020). Performance evaluation of homogeneous charge compression ignition combustion engine – a review. Journal of Engineering and Technological Sciences. https://doi.org/10.5614/j.eng.technol.sci.2020.52.3.1
Mohammed, M. K., Balla, H. H., Al-Dulaimi, Z. M. H., Kareem, Z. S., & Al-Zuhairy, M. S. (2021). Effect of ethanol-gasoline blends on SI engine performance and emissions. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2021.100891
Pera, C., Knop, V., Chevillard, S., & Reveillon, J. (2014). Effects of residual burnt gas heterogeneity on cyclic variability in lean-burn SI engines. Flow, Turbulence and Combustion. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-014-9527-7
Petrucci, L., Ricci, F., Mariani, F., Cruccolini, V., & Violi, M. (2020). Engine Knock Evaluation Using a Machine Learning Approach. SAE Technical Papers, 2020. https://doi.org/10.4271/2020-24-0005
Rakopoulos, C. D., Rakopoulos, D. C., Kosmadakis, G. M., Zannis, T. C., & Kyritsis, D. C. (2023). Studying the cyclic variability (CCV) of performance and NO and CO emissions in a methane-run high-speed SI engine via quasi-dimensional turbulent combustion modeling and two CCV influencing mechanisms. Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.127042
Saikrishnan, V., Karthikeyan, A., & Jayaprabakar, J. (2018). Analysis of ethanol blends on spark ignition engines. International Journal of Ambient Energy, 39(2), 103–107. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2016.1269678
Sasongko, M. N., & Wijayanti, W. (2017). Effect of ethanol addition on the performance and exhaust emissions of a spark ignition engine. Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Sciences. https://doi.org/10.15282/jmes.11.2.2017.14.0248
Sathish Kumar, T., Ashok, B., & Saravanan, B. (2023). Calibration of flex-fuel operating parameters using grey relational analysis to enhance the output characteristics of ethanol powered direct injection SI engine. Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.128340
Sebayang, A. H., Masjuki, H. H., Ong, H. C., Dharma, S., Silitonga, A. S., Kusumo, F., & Milano, J. (2017). Prediction of engine performance and emissions with Manihot glaziovii bioethanol − Gasoline blended using extreme learning machine. Fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.08.102
Shin, S., Lee, Y., Kim, M., Park, J., Lee, S., & Min, K. (2020). Deep neural network model with Bayesian hyperparameter optimization for prediction of NOx at transient conditions in a diesel engine. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2020.103761
Siddeshware, G., Khichade, V., & Lokavarapu, B. R. (2021). Optimization of the parameters influencing the fuel efficiency of SI engine using taguchi method. Materials Today: Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.09.442
Singh, G., Dogra, D., Ramana, R., Chawla, J., Sutar, P. S., Sagare, V. S., Sonawane, S. B., Kavathekar, K., Rairikar, S., & Thipse, S. S. (2021). Development of Dual Fuel (Diesel + CNG) Engine for Off-Road Application. SAE Technical Papers. https://doi.org/10.4271/2021-26-0119
Singh, P. K., Ramadhas, A. S., Mathai, R., & Sehgal, A. K. (2016). Investigation on Combustion, Performance and Emissions of Automotive Engine Fueled with Ethanol Blended Gasoline. SAE International Journal of Fuels and Lubricants, 9(1), 215–223. https://doi.org/10.4271/2016-01-0886
Soe, H., Htike, T. T., & Moe, K. M. (2021). The Effect of Engine Performance of Single Cylinder SI Engine Using Alternative Fuels Due to Various Compression Ratios. IRE Journal, 5(3), 137–144.
Sonawane, S., Sekhar, R., Warke, A., Thipse, S., & Varma, C. (2023). Forecasting of Engine Performance for Gasoline-Ethanol Blends using Machine Learning. Journal of Engineering and Technological Sciences. https://doi.org/10.5614/j.eng.technol.sci.2023.55.3.10
Thakur, A. K., Kaviti, A. K., Mehra, R., & Mer, K. K. S. (2017). Progress in performance analysis of ethanol-gasoline blends on SI engine. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 69(December 2015), 324–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.11.056
Yang, R., Yan, Y., Sijia, R., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Modeling Performance and Emissions of a Spark Ignition Engine with Machine Learning Approaches. 1–13. https://doi.org/10.4271/2022-01-0380.Received
Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Zhong, J., Sun, L., & Meng, T. (2023). Optimum process parameters of IN718 alloy fabricated by plasma arc additive manufacturing using Taguchi-based grey relational analysis. Materials Today Communications. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.107213
Zhou, L., Song, Y., Ji, W., & Wei, H. (2022). Machine learning for combustion. Energy and AI. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyai.2021.100128
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Engineering and Technological Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.