The Behavior of Glued-in Threaded Steel Rod Joints in Bangkirai Timber Beams under Flexural Loading: Experimental and Numerical Investigations
Downloads
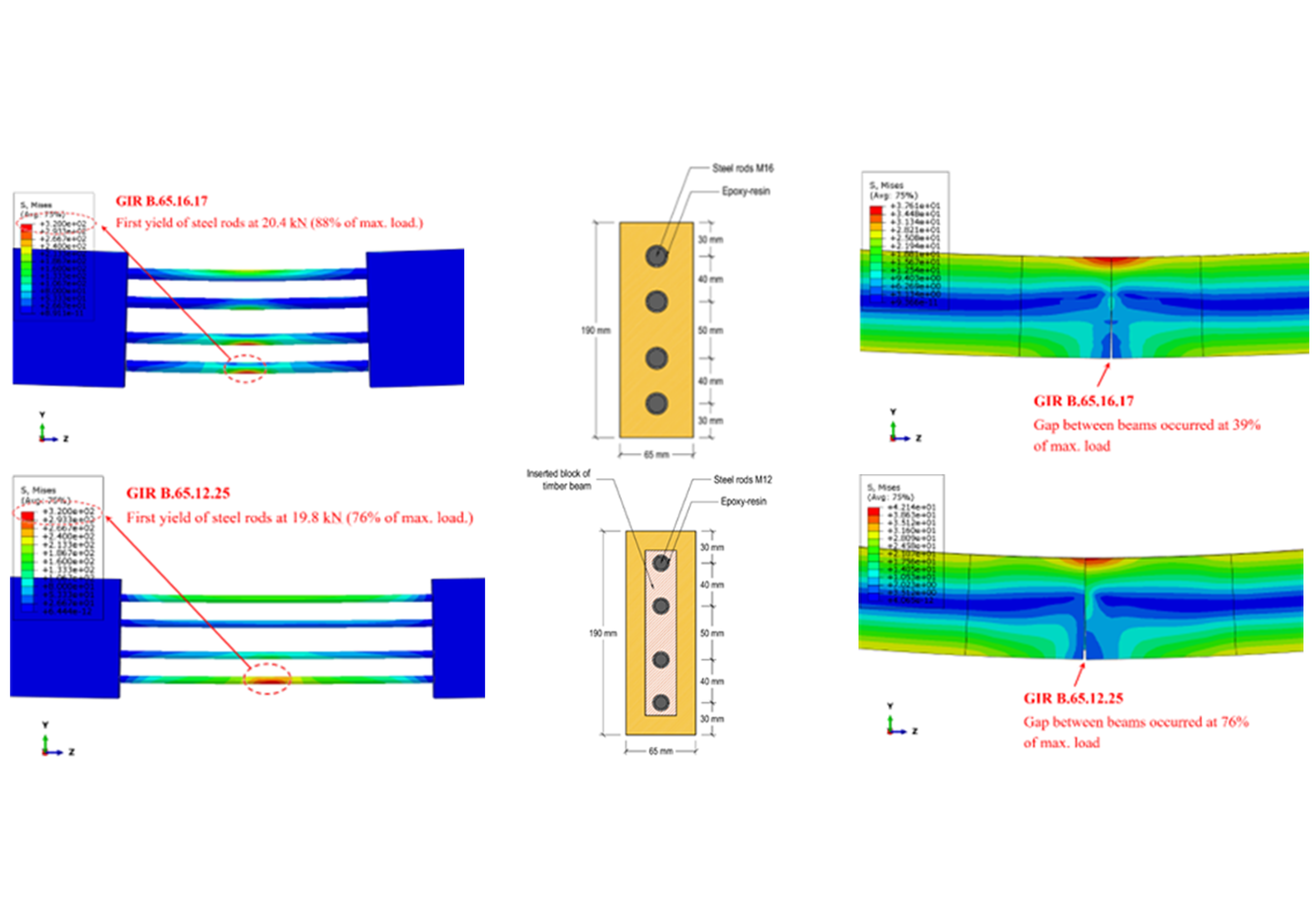
This study investigated flexural performance of Bangkirai timber beams jointed with glued-in threaded steel rods using epoxy-resin adhesive through experimental test and numerical analysis. Six beam specimens were tested under four-point bending with varying rod diameters, anchorage lengths, and beam widths: GIR B.65.16.17 (65 mm width, 16 mm rod, 170 mm anchorage), GIR B.65.12.25 (65 mm width, 12 mm rod, 250 mm anchorage), and GIR B.110.12.25 (110 mm width, 12 mm rod, 250 mm anchorage). The results showed that anchorage length significantly influenced moment capacity and stiffness of the beams. The highest average moment capacity was in GIR B.110.12.25 at 20.08 kNm due to its larger cross-section, while GIR B.65.12.25 showed a 58% higher moment capacity (16.57 kNm) than GIR B.65.16.17 (10.48 kNm). Elastic stiffness values were 538.60 kNm2, 809.44 kNm2, and 948.01 kNm2 in GIR B.65.16.17, GIR B.65.12.25, and GIR B.110.12.25, respectively, with longer anchorage lengths enhancing stiffness. The primary failure mechanism was epoxy-resin bond failure, leading to beam separation, while pull-out failure of steel rods was observed in some cases, particularly in specimens with shorter anchorage lengths. A 3-D nonlinear FEA was developed to validate experimental results. Differences between experimental and FEA results were within acceptable ranges, including 0.6-14.6% for elastic stiffness and 8.1-13.7% for moment capacity. Load-displacement curves obtained from the FEA correlated well with the experimental results, although the model slightly overestimated moment capacity due to the assumption of perfect bonding. These results provided insights for optimizing glued-in rod timber joints in structural applications.
ABAQUS. (2018). Analysis user’s guide volume V: element.
Ali Awaludin, Muhammad Afif Sulhan, Mahmud Kori Effendi, Inggar Septhia Irawati, & Rohana Hassan. (2025). Flexural properties of structural size glulam beams made from Indonesian wood species: experimental programs. Journal of the Korean Wood Science and Technology, 53(3), 287-300.
Ayansola, G. S., Tannert, T., & Vallee, T. (2022). Experimental investigations of glued-in rod connections in CLT. Construction and Building Materials, 324, 126680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.126680
Batchelar, M. L. (2004). Structural joints in glulam. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:46661785
Broughton, J. G., & Hutchinson, A. R. (2001). Pull-out behaviour of steel rods bonded into timber. Materials and Structures, 34(2), 100–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02481558
DIN Deutsches Institut für Normung. (2008). Design of timber structures. General rules and rules for buildings.
EN 408. (2010). Timber structures - Structural timber and glued laminated timber - Determination of some physical and mechanical properties.
Gattesco, N., Gubana, A., Buttazzi, M., & Melotto, M. (2017). Experimental investigation on the behavior of glued-in rod joints in timber beams subjected to monotonic and cyclic loading. Engineering Structures, 147, 372–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2017.03.078
Grunwald, C., Kaufmann, M., Alter, B., Vallée, T., & Tannert, T. (2018). Numerical investigations and capacity prediction of G-FRP rods glued into timber. Composite Structures, 202, 47–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.10.010
Grunwald, C., Vallée, T., Fecht, S., Bletz-Mühldorfer, O., Diehl, F., Bathon, L., Walther, F., Scholz, R., & Myslicki, S. (2019). Rods glued in engineered hardwood products part II: Numerical modelling and capacity prediction. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives, 90, 182–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijadhadh.2018.05.004
Hassanieh, A., Valipour, H. R., Bradford, M. A., & Jockwer, R. (2018). Glued-in-rod timber joints: analytical model and finite element simulation. Materials and Structures, 51(3), 61. https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-018-1189-9
Hussin, T. A. R., Hassan, R., Awaludin, A., Sidek, M. N. M., Hamid, N. H. A., & Salit, M. S. (2022). Experimental bond behaviour of glued-in rod connection for mengkulang glulam under pull-out loading. Civil Engineering and Architecture, 10(3), 1056–1070. https://doi.org/10.13189/cea.2022.100322
Jensen, J. L., Koizumi, A., Sasaki, T., Tamura, Y., & Iijima, Y. (2001). Axially loaded glued-in hardwood dowels. Wood Science and Technology, 35(1–2), 73–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002260000076
Kabir, M. H., Fawzia, S., Chan, T. H. T., & Badawi, M. (2016). Numerical studies on CFRP strengthened steel circular members under marine environment. Materials and Structures, 49(10), 4201–4216. https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-015-0781-5
Kemmsies, M. (1999). Comparison of pull-out strengths of 12 adhesives for glued-in rods for timber structures. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:139337436
Kyvelou, P., Gardner, L., & Nethercot, D. A. (2018). Finite element modelling of composite cold-formed steel flooring systems. Engineering Structures, 158, 28–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2017.12.024
Lavisci, P., Duchanois, G., De Ciechi, M., Spinelli, P., & Feligioni, L. (2003). Influence of glue rheology and joint thickness on the strength of bonded-in rods. Holz Als Roh- Und Werkstoff, 61(4), 281–287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-003-0387-4
Ling, Z., Liu, W., Yang, H., & Chen, X. (2018). Modelling of glued laminated timber joints with glued-in rod considering bond-slip location function. Engineering Structures, 176, 90–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.08.098
Ling, Z., Xiang, Z., Liu, W., Yang, H., & Tang, J. (2019). Load-slip behaviour of glue laminated timber connections with glued-in steel rod parallel to grain. Construction and Building Materials, 227, 117028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117028
Ling, Z., Yang, H., Liu, W., Lu, W., Zhou, D., & Wang, L. (2014). Pull-out strength and bond behaviour of axially loaded rebar glued-in glulam. Construction and Building Materials, 65, 440–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.05.008
Madhoushi, M., & Ansell, M. P. (2008). Behaviour of timber connections using glued-in GFRP rods under fatigue loading. Part I: In-line beam to beam connections. Composites Part B: Engineering, 39(2), 243–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2007.07.001
Malczyk, R. (1993). Glued-in re-bar connection. https://open.library.ubc.ca/collections/831/items/1.0050496
Mindrasari, P., & Awaludin, A. (2018). The effect of diameter and anchorage length of Keruing wooden dowels, deformed steel dowels and GFRP dowels on pull-out strength of Keruing timber block with epoxy resin adhesive. Civil Engineering and Environmental Symposium 2018.
Muciaccia, G. (2019). An experimental approach to determine pull-out strength of single and multiple axially loaded steel rods bonded in glulam parallel to the grain. Wood Material Science & Engineering, 14(2), 88–98. https://doi.org/10.1080/17480272.2017.1404491
Navaratnam, S., Thamboo, J., Ponnampalam, T., Venkatesan, S., & Chong, K. B. (2022). Mechanical performance of glued-in rod glulam beam to column moment connection: an experimental study. Journal of Building Engineering, 50, 104131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2022.104131
Ngudiyono, N., Hariyadi, H., & Ningsih, Y. P. (2021). Numerical simulation of bond strength between steel reinforcement and concrete using Abaqus Student Edition (SE). FROPIL (Forum Profesional Teknik Sipil), 9(1), 10–17. https://doi.org/10.33019/fropil.v9i1.2287 (Text in Indonesian)
O’Neill, C., McPolin, D., Taylor, S. E., Harte, A. M., O’Ceallaigh, C., & Sikora, K. S. (2017). Timber moment connections using glued-in basalt FRP rods. Construction and Building Materials, 145, 226–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.03.241
Otero Chans, D., Cimadevila, J. E., & Gutiérrez, E. M. (2008). Glued joints in hardwood timber. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives, 28(8), 457–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijadhadh.2008.04.008
Parida, G., Johnsson, H., & Fragiacomo, M. (2013). Provisions for Ductile Behavior of Timber-to-Steel Connections with Multiple Glued-In Rods. Journal of Structural Engineering, 139(9), 1468–1477. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0000735
Riberholt, H. (1988). Glued bolts in glulam - proposals for CIB code. Proceedings of the 21st Meeting of W018, Parksville, Vancouver Island, Canada, 19.
Rossignon, A., & Espion, B. (2008). Experimental assessment of the pull-out strength of single rods bonded in glulam parallel to the grain. Holz Als Roh- Und Werkstoff, 66(6), 419–432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-008-0263-3
Serrano E, Steiger R, & Lavisci P. (2008). COST E34-WG1: bonding on site 5 glued-in rods. Lignovisionen, 18, 31–39.
Shekarchi, M., Shakiba, M., Yekrangnia, M., & Tannert, T. (2022). Performance of glued-in rod timber joints under seawater and UV exposure cycles. Construction and Building Materials, 322, 126418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.126418
Steiger, R., Gehri, E., & Widmann, R. (2007). Pull-out strength of axially loaded steel rods bonded in glulam parallel to the grain. Materials and Structures, 40(1), 69–78. https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-006-9111-2
Tannert, T., Vallée, T., & Hehl, S. (2012). Experimental and numerical investigations on adhesively bonded timber joints. Wood Science and Technology, 46(1–3), 579–590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-011-0423-1
Tenar, F. K., Mulyatno, I. P., & Budiarto, U. (2017). Analysis of hull construction joint strength on a 100 GT wooden vessel in the Batang region using the finite element method. Jurnal Teknik Perkapalan, 5(4), 641. http://ejournal3.undip.ac.id/index.php/naval (Text in Indonesian)
Thamboo, J., Navaratnam, S., & Ponnampalam, T. (2022). Pull-out resistance of glued in rod connection in timber: Reliability analyses using an experimental database. Construction and Building Materials, 344, 128291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128291
Tlustochowicz, G., Serrano, E., & Steiger, R. (2011). State-of-the-art review on timber connections with glued-in steel rods. Materials and Structures, 44(5), 997–1020. https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-010-9682-9
Vallée, T., Tannert, T., & Fecht, S. (2017). Adhesively bonded connections in the context of timber engineering – a review. The Journal of Adhesion, 93(4), 257–287. https://doi.org/10.1080/00218464.2015.1071255
Xu, B. H., Bouchaïr, A., & Racher, P. (2012). Analytical study and finite element modelling of timber connections with glued-in rods in bending. Construction and Building Materials, 34, 337–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.02.087
Zhu, H., Faghani, P., & Tannert, T. (2017). Experimental investigations on timber joints with single glued-in FRP rods. Construction and Building Materials, 140, 167–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.02.09
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Engineering and Technological Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.